What Zould You Enter Qt Q Co;;qnd Pro;pt to Start a New Bourneagain Shell Session
Beat out scripting is an of import part of process automation in Linux. Scripting helps you lot write a sequence of commands in a file and so execute them.
This saves you time because you don't take to write certain commands again and over again. You tin can perform daily tasks efficiently and even schedule them for automated execution.
Yous can also gear up certain scripts to execute on startup such every bit showing a particular message on launching a new session or setting certain surround variables.
The applications and uses of scripting are numerous, and so allow's dive in.
In this article, you lot will larn:
- What is a bash beat?
- What is a fustigate script and how exercise you identify it?
- How to create your outset bash script and execute it.
- The basic syntax of shell scripting.
- How to encounter a system's scheduled scripts.
- How to automate scripts past scheduling via cron jobs.
The best fashion to learn is by practicing. I highly encourage you to follow along using Replit. Yous can access a running Linux shell within minutes.
Introduction to the Bash Shell
The Linux control line is provided by a programme called the shell. Over the years, the shell programme has evolved to cater to various options.
Different users can be configured to use unlike shells. But most users prefer to stick with the current default shell. The default beat for many Linux distros is the GNU Bourne-Once again Shell (bash). Bash is succeeded by Bourne shell (sh).
When you first launch the beat, it uses a startup script located in the .bashrc or .bash_profile file which allows yous to customize the behavior of the shell.
When a shell is used interactively, information technology displays a $ when it is waiting for a command from the user. This is called the trounce prompt.
[username@host ~]$
If shell is running equally root, the prompt is changed to #. The superuser shell prompt looks like this:
[root@host ~]#
Fustigate is very powerful every bit it can simplify certain operations that are hard to accomplish efficiently with a GUI. Remember that most servers practice not have a GUI, and it is best to learn to use the powers of a command line interface (CLI).
What is a Bash Script?
A fustigate script is a series of commands written in a file. These are read and executed by the bash program. The program executes line by line.
For example, you lot can navigate to a sure path, create a binder and spawn a process inside it using the command line.
You can do the same sequence of steps by saving the commands in a bash script and running information technology. Yous can run the script any number of times.
How Do You Identify a Bash Script?
File extension of .sh.
By naming conventions, bash scripts end with a .sh. All the same, bash scripts can run perfectly fine without the sh extension.
Scripts offset with a bash blindside.
Scripts are also identified with a shebang. Shebang is a combination of bash # and blindside ! followed the the fustigate vanquish path. This is the get-go line of the script. Shebang tells the trounce to execute it via bash shell. Shebang is but an absolute path to the bash interpreter.
Beneath is an example of the shebang argument.
#! /bin/bash The path of the bash program tin vary. We will see later on how to identify it.
Execution rights
Scripts take execution rights for the user executing them.
An execution right is represented by x. In the case beneath, my user has the rwx (read, write, execute) rights for the file test_script.sh

File colour
Executable scripts appear in a dissimilar colour from rest of the files and folders.
In my instance, the scripts with execution rights announced as green.
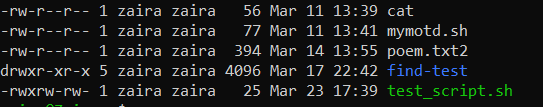
How to Create Your Outset Bash Script
Permit'southward create a simple script in fustigate that outputs Howdy World.
Create a file named hello_world.sh
touch hello_world.sh Detect the path to your bash crush.
which fustigate 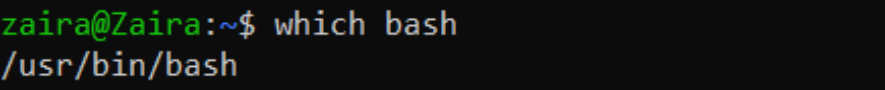
In my case, the path is /usr/bin/bash and I will include this in the shebang.
Write the control.
Nosotros will echo "hello world" to the console.
Our script will wait something similar this:
#! usr/bin/bash echo "Hello World" Edit the file hello_world.sh using a text editor of your option and add the above lines in it.
Provide execution rights to your user.
Modify the file permissions and let execution of the script by using the command below:
chmod u+x hello_world.sh chmod modifies the existing rights of a file for a particular user. We are adding +x to user u.
Run the script.
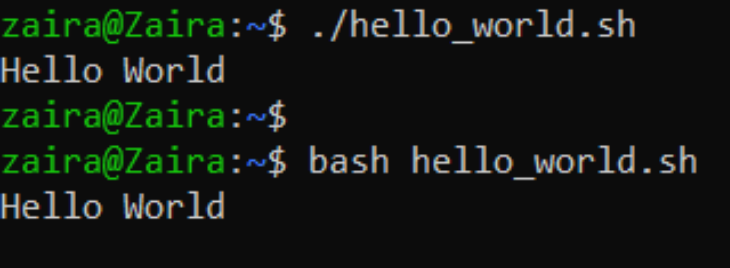
You tin run the script in the following ways:
./hello_world.sh
bash hello_world.sh.
Here's the output:
The Bones Syntax of Fustigate Scripting
Simply similar any other programming language, fustigate scripting follows a set of rules to create programs understandable by the computer. In this section, nosotros will study the syntax of bash scripting.
How to define variables
We can define a variable by using the syntax variable_name=value. To get the value of the variable, add together $ before the variable.
#!/bin/bash # A simple variable example greeting=Howdy proper name=Tux echo $greeting $name 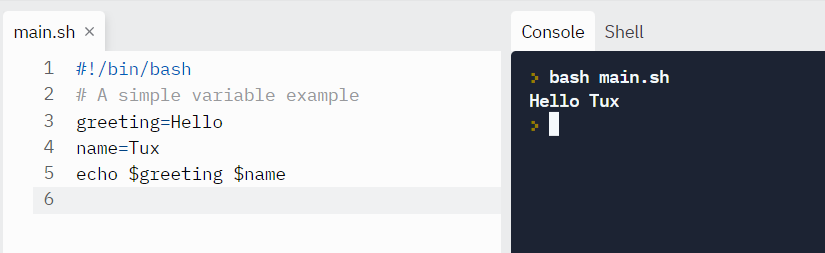
Tux is also the name of the Linux mascot, the penguin.

Arithmetic Expressions
Below are the operators supported past fustigate for mathematical calculations:
| Operator | Usage |
|---|---|
| + | addition |
| - | subtraction |
| * | multiplication |
| / | division |
| ** | exponentiation |
| % | modulus |
Allow'southward run a few examples.
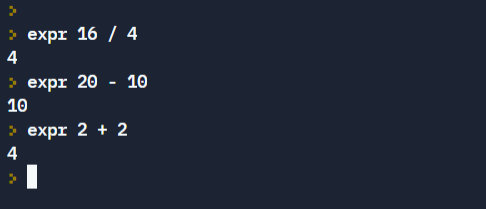
Numerical expressions can also exist calculated and stored in a variable using the syntax below:
var=$((expression))
Allow'southward attempt an case.
#!/bin/bash var=$((3+ix)) repeat $var 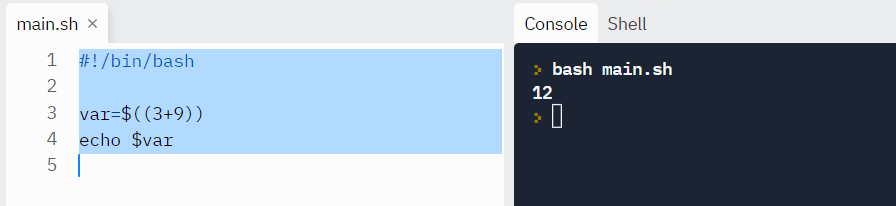
Fractions are not correctly calculated using the in a higher place methods and truncated.
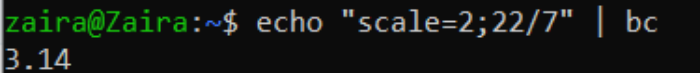
For decimal calculations, we can utilise bc control to get the output to a item number of decimal places. bc (Bash Calculator) is a control line estimator that supports adding upward to a sure number of decimal points.
echo "scale=2;22/7" | bc
Where scale defines the number of decimal places required in the output.
How to read user input
Sometimes yous'll demand to assemble user input and perform relevant operations.
In bash, we tin can have user input using the read command.
read variable_name To prompt the user with a custom message, apply the -p flag.
read -p "Enter your historic period" variable_name
Instance:
#!/bin/bash repeat "Enter a numner" read a repeat "Enter a numner" read b var=$((a+b)) echo $var 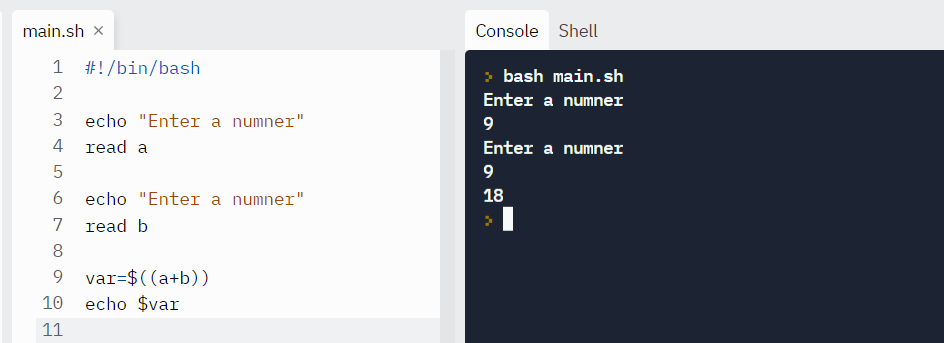
Numeric Comparison logical operators
Comparison is used to check if statements evaluate to true or false. We can use the below shown operators to compare two statements:
| Operation | Syntax | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Equality | num1 -eq num2 | is num1 equal to num2 |
| Greater than equal to | num1 -ge num2 | is num1 greater than equal to num2 |
| Greater than | num1 -gt num2 | is num1 greater than num2 |
| Less than equal to | num1 -le num2 | is num1 less than equal to num2 |
| Less than | num1 -lt num2 | is num1 less than num2 |
| Not Equal to | num1 -ne num2 | is num1 non equal to num2 |
Syntax:
if [ conditions ] then commands fi Example:
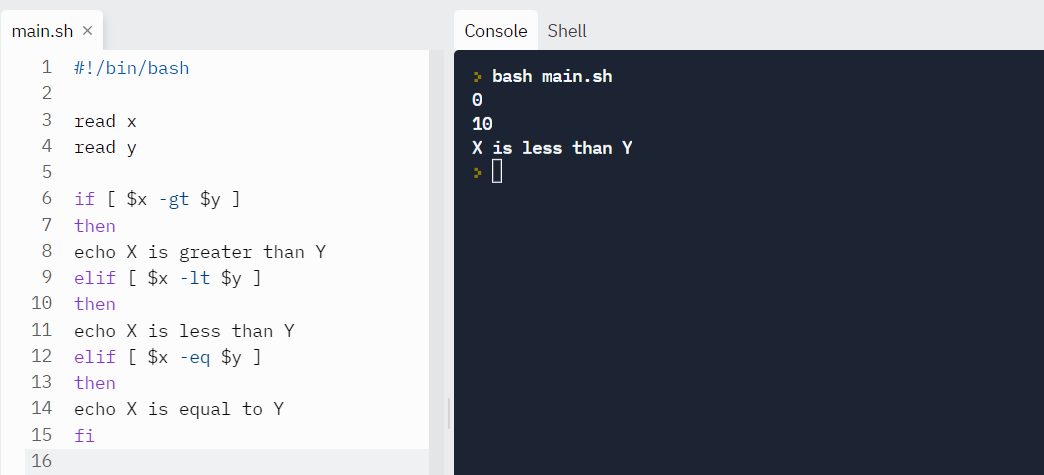
Permit'southward compare two numbers and find their human relationship:
read x read y if [ $x -gt $y ] then echo X is greater than Y elif [ $x -lt $y ] and then echo X is less than Y elif [ $10 -eq $y ] so repeat X is equal to Y fi Output:
Conditional Statements (Determination Making)
Conditions are expressions that evaluate to a boolean expression (true or simulated). To check conditions, we can use if, if-else, if-elif-else and nested conditionals.
The structure of conditional statements is as follows:
-
if...and then...fistatements -
if...then...else...fistatements -
if..elif..else..fi -
if..then..else..if..then..fi..fi..(Nested Conditionals)
Syntax:
if [[ condition ]] then statement elif [[ status ]]; so statement else do this past default fi To create meaningful comparisons, we can apply AND -a and OR -o likewise.
The below statement translates to: If a is greater than 40 and b is less than 6.
if [ $a -gt xl -a $b -lt 6 ]
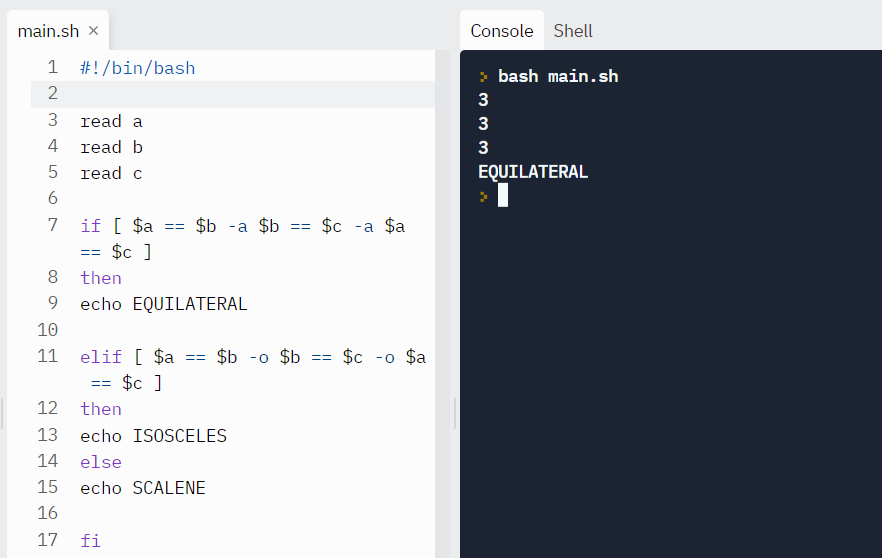
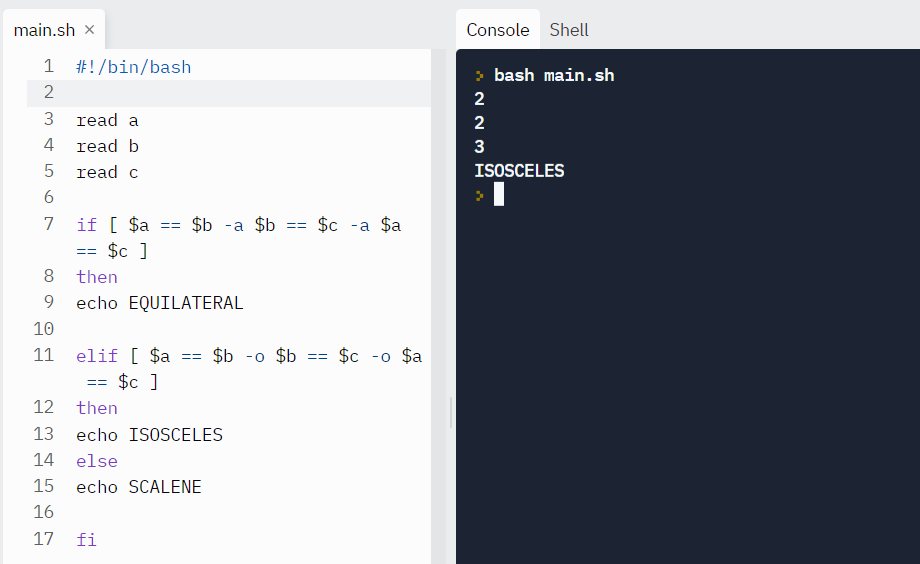
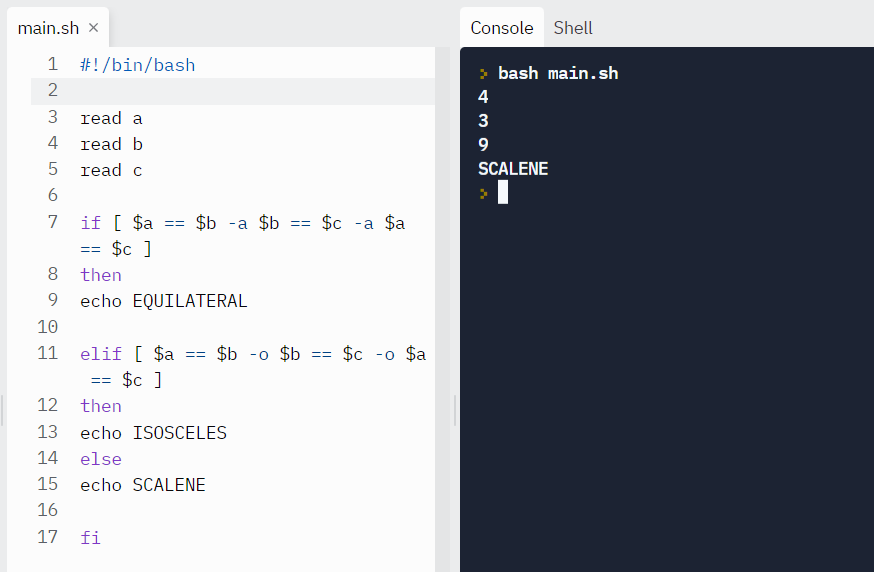
Instance: Let's find the triangle type by reading the lengths of its sides.
read a read b read c if [ $a == $b -a $b == $c -a $a == $c ] then echo EQUILATERAL elif [ $a == $b -o $b == $c -o $a == $c ] then echo ISOSCELES else echo SCALENE fi Output:
Test case #1
Exam case #2
Test case #iii
Looping and skipping
For loops allow you to execute statements a specific number of times.
Looping with numbers:
In the example below, the loop will iterate five times.
#!/bin/fustigate for i in {1..5} do repeat $i done Looping with strings:
We can loop through strings also.
#!/bin/bash for X in cyan magenta yellowish do echo $Ten washed 
While loop
While loops bank check for a status and loop until the condition remains true. Nosotros need to provide a counter statement that increments the counter to control loop execution.
In the example below, (( i += 1 )) is the counter statement that increments the value of i.
Example:
#!/bin/bash i=1 while [[ $i -le 10 ]] ; do repeat "$i" (( i += 1 )) done 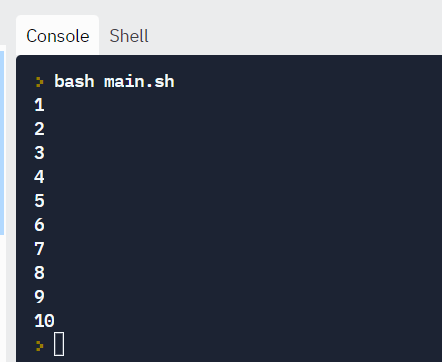
Reading files
Suppose we have a file sample_file.txt equally shown below:

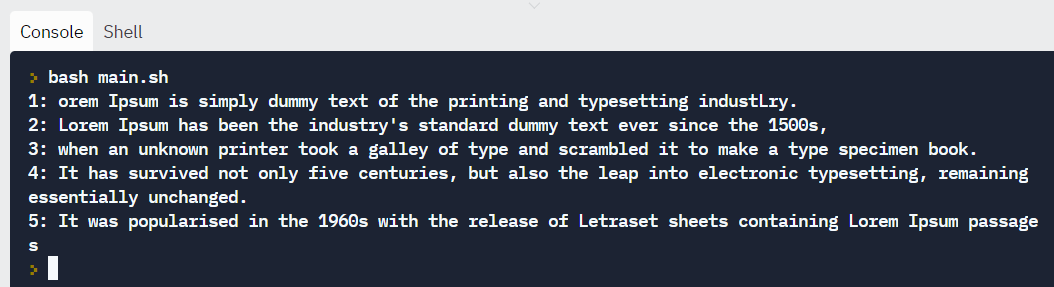
We can read the file line by line and print the output on the screen.
#!/bin/bash LINE=1 while read -r CURRENT_LINE practice echo "$LINE: $CURRENT_LINE" ((LINE++)) done < "sample_file.txt" Output:
How to execute commands with back ticks
If you need to include the output of a complex command in your script, you lot can write the statement inside dorsum ticks.
Syntax:
var= ` commands `
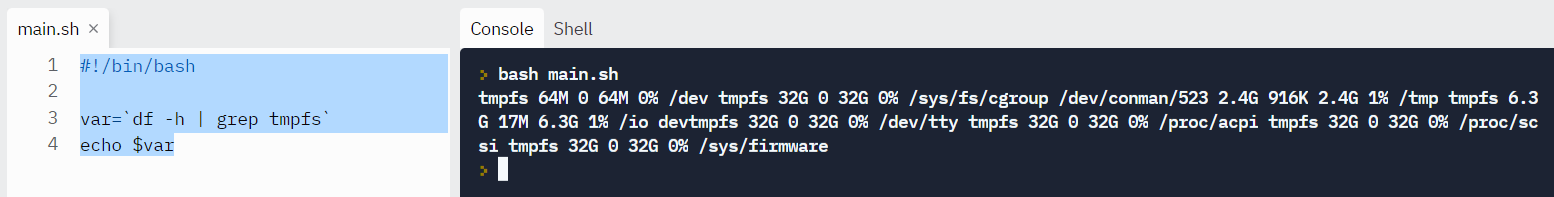
Example: Suppose nosotros want to get the output of a listing of mountpoints with tmpfs in their name. We can arts and crafts a statement like this: df -h | grep tmpfs.
To include it in the fustigate script, we can enclose it in back ticks.
#!/bin/fustigate var=`df -h | grep tmpfs` echo $var Output:
How to become arguments for scripts from the command line
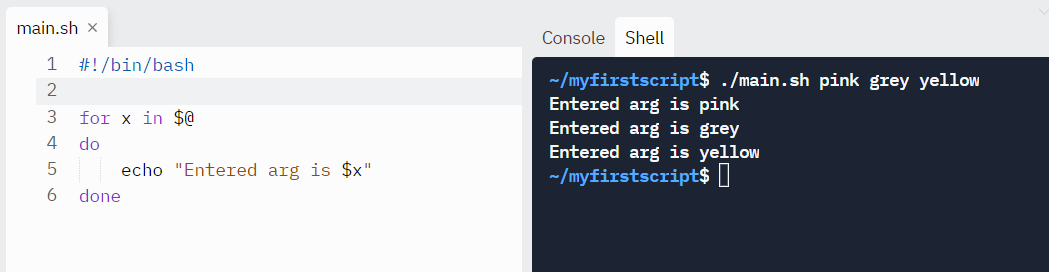
It is possible to give arguments to the script on execution.
$@ represents the position of the parameters, starting from one.
#!/bin/bash for x in $@ exercise echo "Entered arg is $x" washed Run information technology like this:
./script arg1 arg2
How to Automate Scripts by Scheduling via cron Jobs
Cron is a chore scheduling utility present in Unix like systems. You can schedule jobs to execute daily, weekly, monthly or in a specific fourth dimension of the day. Automation in Linux heavily relies on cron jobs.
Below is the syntax to schedule crons:
# Cron job example * * * * * sh /path/to/script.sh Hither, * stand for represents minute(s) 60 minutes(s) day(south) calendar month(s) weekday(s), respectively.
Beneath are some examples of scheduling cron jobs.
| SCHEDULE | SCHEDULED VALUE |
|---|---|
| 5 0 * 8 * | At 00:05 in August. |
| v four * * half-dozen | At 04:05 on Sunday. |
| 0 22 * * 1-5 | At 22:00 on every day-of-week from Monday through Friday. |
You can learn about cron in detail in this blog post.
How to Check Existing Scripts in a System
Using crontab
crontab -fifty lists the already scheduled scripts for a particular user.
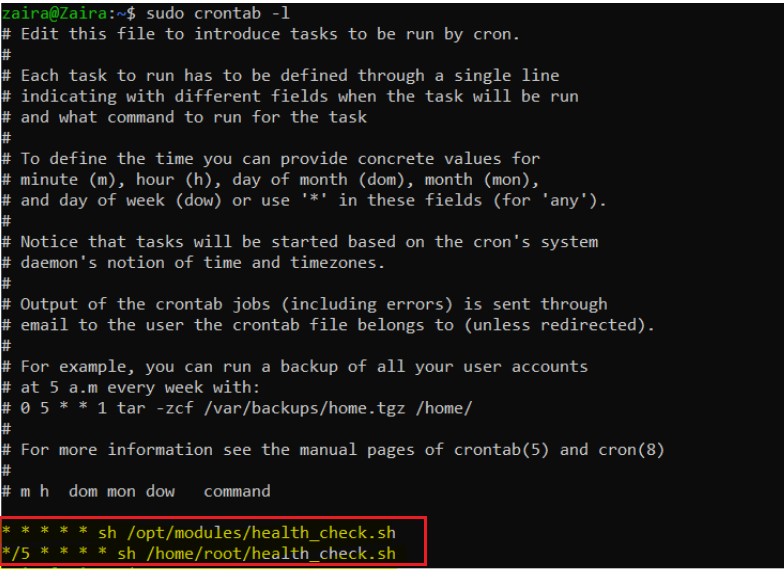
Using the find command
The detect command helps to locate files based on certain patterns. As about of the scripts finish with .sh, nosotros tin can apply the observe script like this:
discover . -type f -name "*.sh" Where,
-
.represents the current directory. You can change the path accordingly. -
-type findicates that the file blazon nosotros are looking for is a text based file. -
*.shtells to lucifer all files catastrophe with.sh.
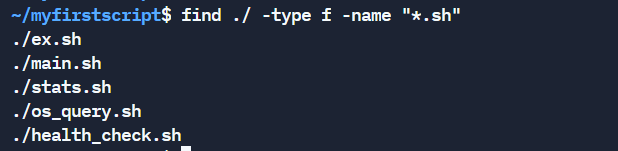
If yous are interested to read about the detect command in item, check my other mail.
Wrapping upwards
In this tutorial we learned the basics of crush scripting. Nosotros looked into examples and syntax which tin can help united states write meaningful programs.
What's your favorite thing you learned from this tutorial? Let me know on Twitter!
You tin can read my other posts here.
Work vector created by macrovector - www.freepik.com
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp'south open source curriculum has helped more than xl,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
Source: https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/shell-scripting-crash-course-how-to-write-bash-scripts-in-linux/
0 Response to "What Zould You Enter Qt Q Co;;qnd Pro;pt to Start a New Bourneagain Shell Session"
แสดงความคิดเห็น